ATMOSPHERIC RADIATION
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The main goal of the project is the identification of well-characterized case studies aimed at a radiative self-consistency experiment of ice clouds and in mixed phase on the Antarctic Plateau, as well as the improvement of current spectral patterns in the far-infrared region. This can be achieved through the synergistic use of various measurement instruments operating in different bands of the electromagnetic spectrum and installed at the Concordia base, particularly at the Physics shelter. The infrared radiation emitted by the atmosphere and clouds is measured by the Fourier transform spectroradiometer REFIR-PAD (Radiation Explorer in Far Infrared - Prototype for Applications and Development) operating at Concordia since 2012 inside the DoCTOR PNRA project by Dr. Giovanni Bianchini (https://www.pnra.aq/it/project/330/dome-c-tropospheric-observer-osservatorio-troposferico-dome-c). The position and phase of clouds is estimated by the backscattering and depolarization LIDAR active since 2008. The particle size distribution can be estimated by an ICE- CAMERA, i.e., a kind of optical scanner that collects precipitating ice crystals on the shelter roof. As of the 2018-2019 campaign, a 24 GHz weather radar (Micro Rain Radar, MMR) operating continuously has been installed on the roof of Physics, which can provide an estimate of the precipitation rate of ice crystals and the falling velocities of those crystals. From these measurements, efforts are also being made to estimate the ice content in the case of precipitating ice clouds. Finally, during the last 2019-2020 campaign, a HALO-CAMERA was also installed, which can provide an estimate of the shape of ice crystals that can be used as a priori information in transfer models radiative suitable for simulating the effect of clouds. In order to complete the radiative closure (or self-consistency) experiment, the idea is to use the values of the parameters of the precipitating ice clouds, i.e., optical thickness and effective diameter, obtained from the inversion of the spectra produced by REFIR-PAD, to characterize the size distribution of the ice crystals and use the latter to calculate the reflectivity at the MRR radar wavelength, i.e., 24 GHz. The calculation of reflectivity obviously depends on the type of particles (habit) that are assumed, so the inversion procedure of the spectra produced by REFIR-PAD is repeated assuming different types of particles, thus using different optical property databases depending on whether aggregates, bullet rosettes, hexagonal columns, platelets or hollow columns are used. Consequently, the same habit assumptions will have to be made for the calculation of radar reflectivity. The reflectivity obtained can at this point be compared with the experimental reflectivity measured by MRR. Data analysis was carried out by Dr. Alessandro Bracci of ISAC-CNR and Giacomo Roversi of Ca' Foscari University of Venice, both belonging to the group led by Dr. Luca Baldini. Unfortunately, the very small size of the crystals at Concordia, due to the extremely low temperatures and very low humidity values, make it difficult to detect many of these crystals. For this reason, an initial work involved precisely the selection of optimal cases that could be analyzed. The work appears to be still in progress although positive results have already been obtained from the retrieval products of REFIR-PAD, which have allowed the estimation of the reflectivity at 24 GHz, which has been compared ,in the cases of best radar signal, with that measured by MRR obtaining a good agreement. The backscattering signal allows to derive the top and bottom elevations of the cloud to be fixed in the simulation of the radiative transfer. The depolarization signal makes it possible to discriminate the presence of ice, as water droplets do not produce depolarization signal. The lidar data, along with halo-camera and ice-camera data, are provided by Dr. Massimo Del Guasta.
-
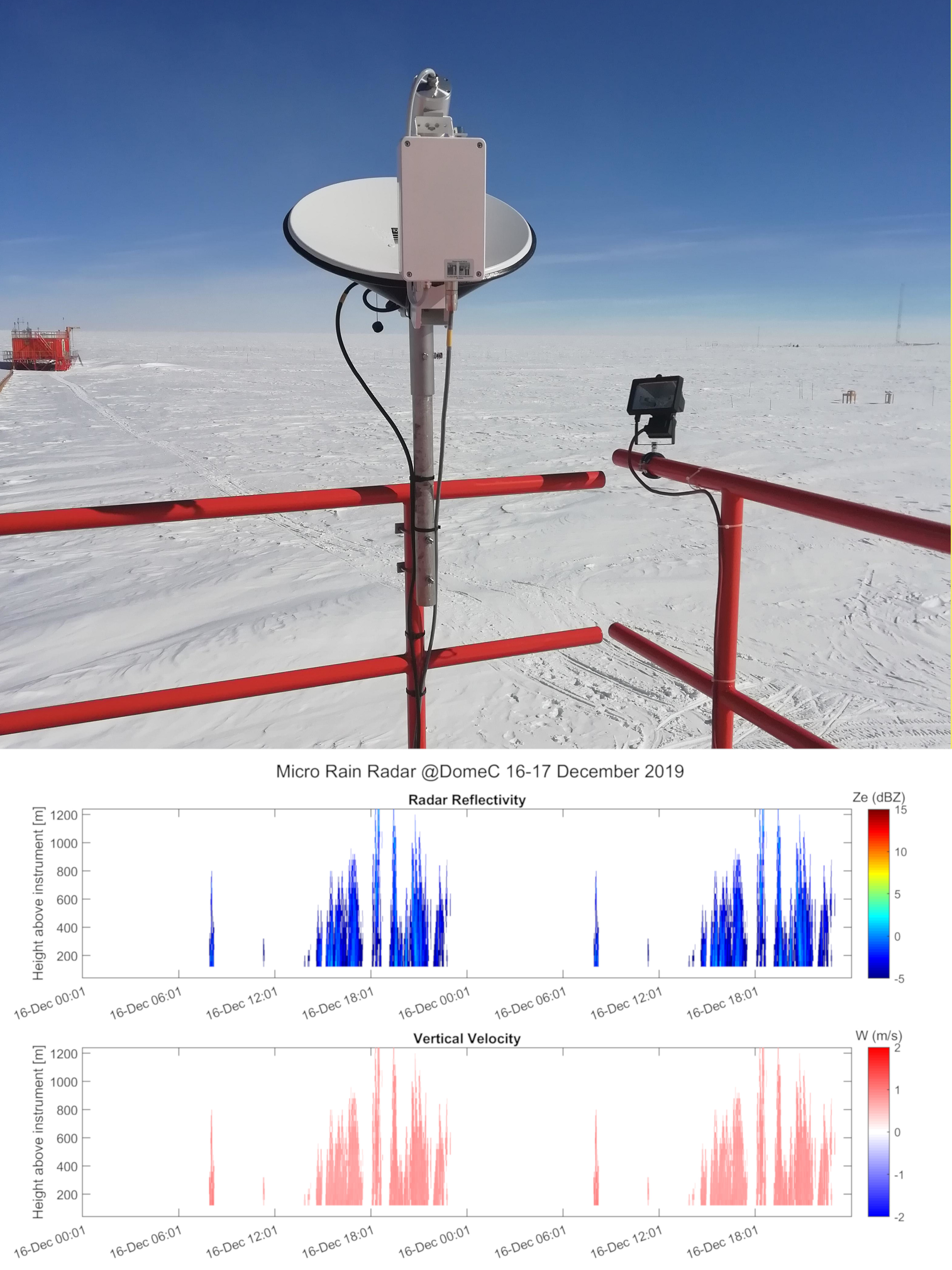
Vertical profiles along the first three kilometres of atmosphere above the ground (from 300 to 3000 m a.g.l.) of equivalent radar reflectivity factor (Ze), Doppler velocity (W) and Doppler spectral width (Sw) from a 24-GHz vertically pointing Micro Rain Radar MRR-2 by METEK GmbH positioned at Concordia Station (Dome C, Antarctica). The main objective of the FIRCLOUDS project is a complete spectral characterization of cirrus and mixed phase clouds in order to evaluate the radiative models in the FIR regime, where the clouds effect is very strong, and systematic spectral measurements are scarcely available. The micro rain radar (MRR) data allows the determination of the clouds reflectivity and the vertical velocity of ice crystals in the cases of precipitating clouds.
-

Pictures of the ice camera and the halo camera positioned at Concordia Station (Dome C, Antarctica). Data are available on the INO-CNR server on request to Dr. Massimo Del Guasta. The main objective of the FIRCLOUDS project is a complete spectral characterization of cirrus and mixed phase clouds in order to evaluate the radiative models in the FIR regime, where the clouds effect is very strong, and systematic spectral measurements are scarcely available. The ice and halo imager cameras enable an assessment of the cloud ice crystals micro-physics.
-
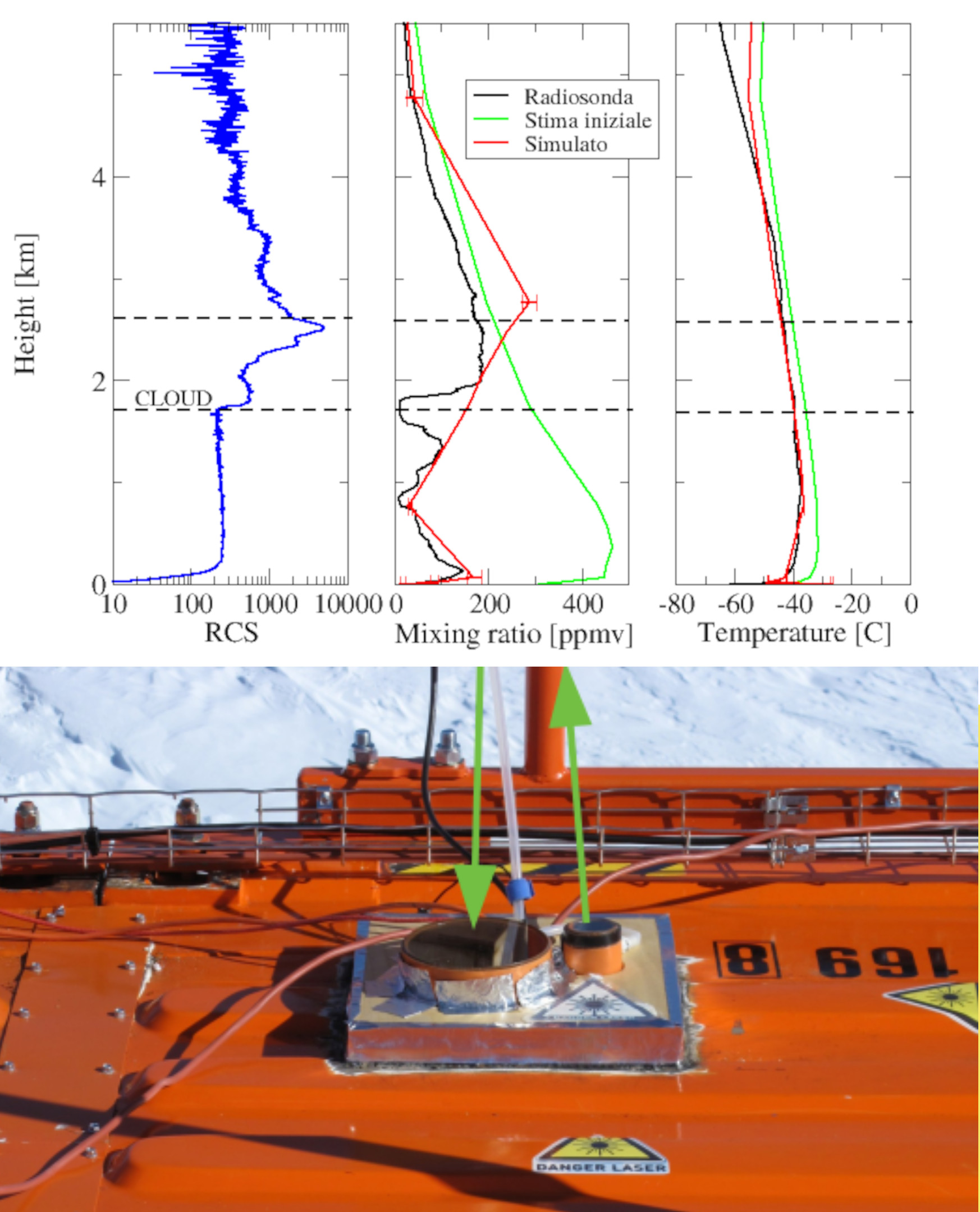
Backscattering and depolarization data from a LIDAR positioned at Concordia Station (Dome C, Antarctica). Data are available on the INO-CNR server on request to Dr. Massimo Del Guasta. The main objective of the FIRCLOUDS projectis a complete spectral characterization of cirrus and mixed phase clouds in order to evaluate the radiative models in the FIR regime, where the clouds effect is very strong, and systematic spectral measurements are scarcely available. A backscattering/depolarization lidar contributes to the estimation of the clouds position and phase, and of the optical extinction profile.
-
The current vision of global climatic changes stresses on the interlinked action of many factors, often more evident at regional scales. Polar regions are among the areas most sensitive to perturbations of the climate: through connections involving ocean, atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere and cryosphere, they respond to, amplify, and drive changes elsewhere in the Earth system, so that understanding their role is essential. Peculiar characteristics of Polar Regions contribute to modify the energy and radiation budget, and the characteristics of the polar atmospheric boundary layer (ABL), increasing relevance at regional level of coupling processes between components of the climate system, especially in the coastal region. In particular, the long polar night, the sea-ice and snow coverage, favouring the persistency of stable atmospheric conditions, and the local and mesoscale circulation interactions, all affect the status and variability at different time scales of components of the regional climate system. Predicting future conditions of the polar regions is the goal of the Polar Prediction Project and of one of its key elements, the Year of Polar Prediction (YOPP, http://www.polarprediction.net/yopp.html), scheduled to take place from mid-2017 to mid-2019). This requires the scientific knowledge of their present status as well as a process-based understanding of the mechanisms of change. The parameterization of physical processes in regional and global hydrodynamical numerical models of the atmosphere is not yet enough accurate for a correct representation of all components of the climatic system and of their connections, the knowledge of which is needed to determine the role of polar regions in the global climate. As an example, more extended and integrated dataset are required to improve the parameterization of the ABL, for complex orography areas such as the polar coastal regions. The general scope of this project is to improve the understanding of the surface-atmosphere mass and energy exchanges at an Antarctic coastal site in the Ross Sea through continuous and accurate measurements of the atmospheric parameters, and development and verification of multiscale modelling, and through these activities, to address some of the relevant questions included in the roadmap for Antarctic and Southern Ocean science for the next two decades and beyond. Measurements will be carried out year-round at the new Korean Jang Bogo Antarctic Research Station (JBS), located at the coast of Terra Nova Bay, in the vicinity of the Italian Mario Zucchelli Station. Measurement and analysis of radiation components, atmospheric constituents and energy fluxes, meteorological and micrometeorological parameters, will be implemented jointly by Korea Polar Research Institute (KOPRI), CNR and UNIFI, in a way similar to the collaboration already active in the Arctic. Such implementation will be very useful to close a gap in the global climate observation system (GCOS) and contribute to WMO programs providing scientific data and information on meteorological and radiation regimes, vertical structure and chemical composition of the atmosphere.