1
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
Antarctic ecosystems have a high number of species, that are closely linked to the presence of sea ice and seasonal cycles. This biodiversity is subject to anthropogenic and natural influences. Zooplankton communities can provide a static snapshot of the health of the ecosystem. Zooplankton samples were collected with a 200 μm mesh net at 3 different sampling points at 80 m depth.
-
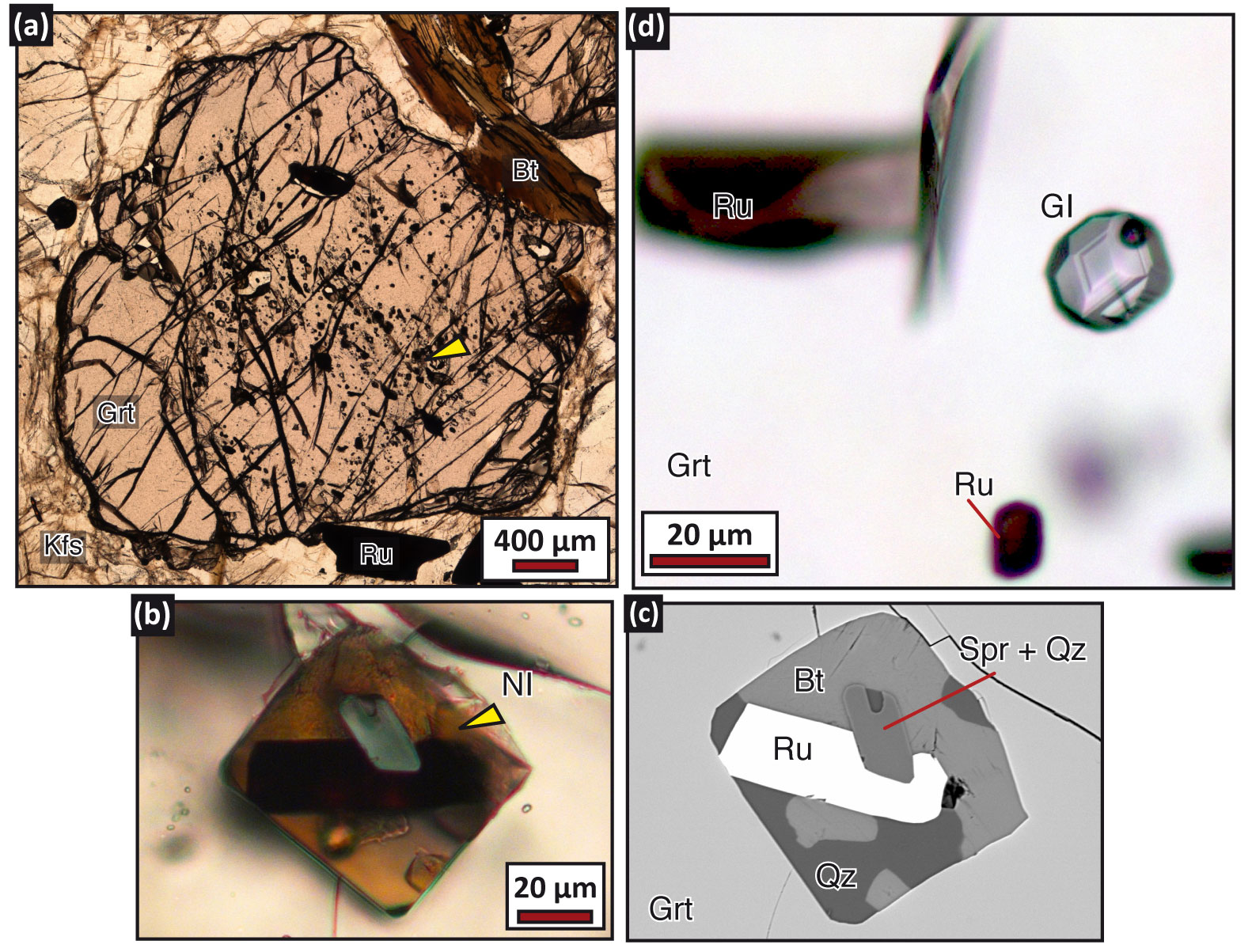
Below the results obtained by the HOT ANTARCTICA project are presented. Results regarding geochemistry of crustal melts Main results obtained by the most prominent samples are described separately for each of the investigated terranes (Napier Complex, Lützow Holm Complex, Rauer Islands and Schrimacher Hills). The methodology employed during the work is also listed below: 1) Samples interrogated in this project were previously collected from Napier Complex (provided by the collaboration with Prof. Simon Harley, University of Edinburgh), Lützow Holm Complex (provided by the collaboration with Prof. Satish-Kumar, University of Niigata), Rauer Islands (provided by the collaboration with Prof. Simon Harley, University of Edinburgh and in collaboration with Zhao Liu, Northwest University ,China) and Schrimacher Hills (provided by the Museo Nazionale dell’Antartide, Siena, Italy). 2) Microstructural and petrographic study were done in all samples to identify equilibrium assemblages, melting reaction microstructures and occurrence of nanogranitoids (i.e. crystallized inclusions), melt and fluid inclusions. 3) Microstructural characterization of inclusions using Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM) analyses were done: i) to identify the submicrometric phases within nanogranitoids and ii) to verify the homogeneity of remelted nanogranites and preserved glassy melt inclusions. 4) Experimental remelting of crystallized melt inclusions was performed to overcome the problem of MI decrepitation and volatile loss. The remelting of nanogranitoids was performed at high pressure with a piston cylinder apparatus using a QUICKpress piston cylinder apparatus produced by Depths of the Earth (installed at the Dipartimento di Geoscienze, UniPd). 5) Analysis of the major and trace elements contents of melt inclusions was carried out using i) an electron microprobe at the at University of Milan and ii) a LAICPMS at University of Perugia. 6) Thermodynamic modeling of anatectic conditions: the evaluation of P-T-X parameters and of P-T paths in the different geologic contexts were carried out using the software Perple_X. 7) Micro-Raman spectroscopy: characterization of fluid inclusions coexisting with melt inclusions was done using a HORIBA LabRam HR (high resolution) Raman microspectrometer at the University of Pavia. 8) Cross-comparison of data: during the development of this research project all collected data were analyzed by cross-comparing the information from the different geological contexts, with the aim to highlight similarities and differences. 9) Data discussion and evaluation: all data was analyzed and discussed in tight collaboration with the researchers involved in this project. 10) Synthesis and dissemination of results: dissemination of results was done with oral and poster presentations in several international conferences (see list on the appropriate section - Atti). Presentations include invited keynote presentations by the PI, Bruna Borges Carvalho at Goldschmidt (France, 2023) and Hutton Symposium (Italy, 2023). Invited seminars were also given in several important universities around the world [University of Bern, Switzerland; University of Cambridge, UK; University of Niigata, University of Kyoto, Japan]. Furthermore, a total of two research papers have been published in journals of high impact factor, and other two articles are in preparation. Here we also provide mineral, geochemical and geochronological data of studied areas at Rundvagshetta and Rauer Islands. Preprinted versions of two published article where the data is explained are also provided. Carvalho, B.B., Bartoli, O., Cesare, B., Satish-Kumar, M., Petrelli, M., Kawakami, T., Hokada, T., Gilio, M. (2023). Revealing the link between A-type granites and hottest melts from residual metasedimentary crust. Geology 51, 845-849. https://doi.org/10.1130/G51097.1 Liu, Z., Carvalho, B.B., Li, W., Tong, L., Bartoli, O., Li, C., Chen, L., ,Yan, Q, Wu, H. 2023. Into the high to ultrahigh temperature melting of Earth’s crust: Investigations of melt and fluid inclusions within Mg–rich metapelitic granulites from the Mather Peninsula, East Antarctica. Journal of Petrology 64, egad051. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egad051 Results regarding petrology and geochronology of granulites In northern Victoria Land, the presence of two contrasting P-T paths suggests the possibility that high-grade complexes could have experienced a different metamorphic evolution both in space and time. Geochronological data of the Granite Harbour Intrusives support a prolonged magmatic activity (540-480 Ma), with multiple igneous pulses. This could imply the existence of magmatic underplating triggering the development of monometamorphic granulites during the Ross Orogeny. On the other hand, structural and PT evolution suggest the presence of a polymetamorphic granulitic belt that could be remnant of older orogeny as the Panafrican (ca. 600-500 Ma) (Lombardo et al., 1987; Palmeri, 1997; Talarico and Castelli, 1995). In order to discriminate mono- from poly-metamorphic evolution, metasedimentary granulite complex from the Deep Freeze Range has been investigated. Among all available granulite samples, a detailed petrographical study has been conducted to select the most representative and suitable HT granulite-facies rocks: four samples have been individuated for petrological and geochronological analyses (Opx-Grt and >30 µm Zrn/Mnz bearing), fifteen for geochemistry (absence of leucosome). In the Deep Freeze Range, HT granulites consist of Grt-Opx±Bt±Crd±Spl±Crn gneisses characterized by the presence of numerous Opx±Grt leucocratic segregations. Geochemical results confirm that analyzed granulite protholites have sedimentary origin, being comparable to Post Archean Australian Shale (PAAS; Taylor and McLennan, 1985), and they have been deposited in an orogenic setting (active continental margin). Petrographical, microstructural and mineral chemistry analyses show a metamorphic evolution including three different stages: Pl-Grt1-Spl-Crn-Ilm medium-P granulite facies (M1), Qtz-Pl-Opx-Grt1-Crd-Ilm-Kfs low-P granulite facies (M2), and Qtz-Pl-Grt2-Kfs-Bt-Ath low-P amphibolite (M3). Preliminary petrological results indicate that evolving metamorphic parageneses describe an initial isothermal decompression (exhumation event) followed by isobaric cooling; further thermodynamic modeling by software Perple_X will allow to better define P-T-X conditions. Geochronological studies involved the observation and analysis of monazites and zircons on four selected granulite thin sections. Investigations included X-ray mapping carried out under the electron microscope, CL-BSE imaging (zircons), and trace element analysis and U-Pb dating using LA-ICP-MS. Acquired data are still under review and will have a fundamental role in the reconstruction of the P-T-t path, thus making it possible to discriminate between mono- and poly-metamorphic hypotheses. References Lombardo et al 1987. Memorie della Società Geologica Italiana 33, 99-130. Palmeri R. 1997. Lithos 42, 47-66. Talarico and Castelli D. 1995. Precamb. Res. 75, 157-174. Taylor and McLennan S.M. 1985. Blackwell, Oxford, 312 p.
-
We will collect stool samples from the volunteers at the Mario Zucchelli Station at different time points. The samples will be analysed by shotgun metagenomic sequencing, considering only the microbial component.
-
Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), characterized by a moltitude of ice tongues flowing from land to sea, represents an ideal study site for understanding the complex interaction between relative sea level variations and ice sheet dynamics during the Holocene. The DISGELI project, thanks to the combination of innovative technology and traditional methods for geomorphologic and stratigraphic analysis, aims to: i) reconstruct the local variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet after the Last Glacial Maximum; ii) provide a time constrain for the deglaciation processes along the coast; iii) reconstruct, with unprecedent detail, the relative sea level variations during Holocene in the Drygalski basin. The morpho-bathymetric and topographic data obtained through this study will be integrated using digital terrain models based on the analyses of key areas onland, where palaeo-coastlines and sea-level markers have been identified.
-
Calibrated (in unit of solar disk brightness) measurements of the sky brightness at DOME C as obtained by the ESCAPE experiment during the campaign 2022-2023
-
We will collect skin samples from the volunteers at the Mario Zucchelli Station at different time points, using safe and not harmfull kits. Samples will be analysed by shotgun metagenomic sequencing, considering only the microbial component.
-
Antarctic ecosystems have a high number of species, that are closely linked to the presence of sea ice and seasonal cycles. This biodiversity is subject to anthropogenic and natural influences. Macrozoobenthic communities are the 'biological memory' of the ecosystem, structuring themselves as a function of environmental changes over the years. Macrozoobenthos samples were collected using suction dredging and scraping techniques, in soft and hard bottoms. Sampling occurred in 5 different sites.
-
We will collect oral samples from the volunteers at the Mario Zucchelli Station at different time points, using safe and not harmfull kits. Samples will be analysed by shotgun metagenomic sequencing, considering only the microbial component.
-

Trophic interactions underlie coexistence mechanisms between species and affect biodiversity and heavy metal bioaccumulation processes. Sea ice dynamics, which at Terra Nova Bay is characterized by an extraordinary seasonality, drives interspecific interactions. Indeed, the activation of the primary production after sea-ice break up opens alternative trophic pathways for consumers. By means of C and N stable isotope analyses, the present project aims at (i) determining food web structure at Terra Nova Bay at different bathymetries and in opposite sea-ice cover conditions; (ii) evaluating heavy metal bioaccumulation in species along food chains, including fish of commercial interests, both in the presence and absence of photosynthetic primary producers. The hypothesis to be tested is if the activation of primary producers following sea-ice break up significantly modifies the food web structure and stability against species loss, as well as heavy metals concentration along food chains. Data on Antarctic food webs are scarce, and even scarcer is our knowledge on mechanisms of primary and secondary biodiversity loss and biomagnification processes in invertebrates and fish. The present research project will shed light on mechanisms underlying biodiversity maintenance in the Antarctic ecosystem and on risks for human health related to heavy metals accumulation in fish species currently or potentially exploited commercially, also in light of expected changes in the extension of sea ice cover. A valuable reference baseline will be established for future studies at the Italian Antarctic Station and for the Marine Protected Area in the Ross Sea.
-
Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), characterized by a moltitude of ice tongues flowing from land to sea, represents an ideal study site for understanding the complex interaction between relative sea level variations and ice sheet dynamics during the Holocene. The DISGELI project, thanks to the combination of innovative technology and traditional methods for geomorphologic and stratigraphic analysis, aims to: i) reconstruct the local variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet after the Last Glacial Maximum; ii) provide a time constrain for the deglaciation processes along the coast; iii) reconstruct, with unprecedent detail, the relative sea level variations during Holocene in the Drygalski basin. The morpho-bathymetric and topographic data obtained through this study will be integrated using digital terrain models based on the analyses of key areas onland, where palaeo-coastlines and sea-level markers have been identified.