environment
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-

The research program aims to continue accurate measurements of surface radiative fluxes downwelling and upwelling at Dome-C, within the network Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN https://bsrn.awi.de/), in order to provide broadband measurements of solar radiation short wave (in the three downwelling components direct, diffuse, global and in the global reflected fluxes) and thermal radiation (emitted from the atmosphere and from the surface). These measurements performed throughout the year provide complete information of the radiative regime in the East Antarctic Plateau, as well as its seasonal and interannual variability, and the radiative fluxes are an important input parameter for both the mass balance and regional climate models. In addition, the surface irradiance datasets are required to validate and calibrate at least 10-11 different satellite observations.
-
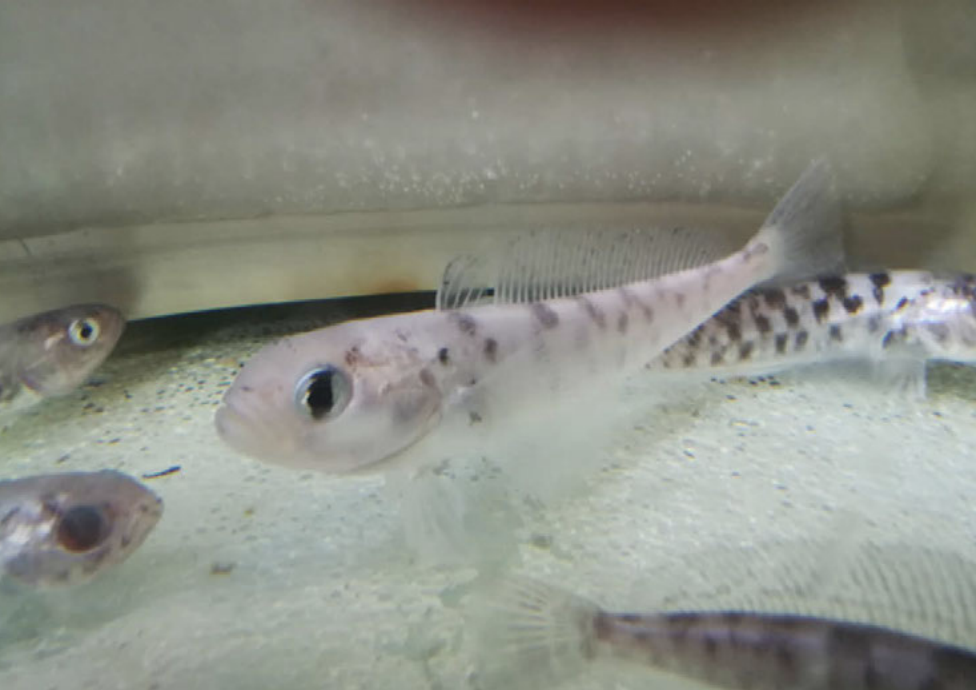

Trophic interactions underlie coexistence mechanisms between species, define the functional role of specie within communities, affect biodiversity and bioaccumulation processes of heavy metal. Sea-ice dynamics, which at Terra Nova Bay is characterized by an extraordinary seasonality, drives interspecific interactions and the exchange of materials between ecosystem compartments. Indeed, the activation of the primary production after sea-ice break up opens alternative trophic pathways for consumers. The “next generation SRPs” represent a highly appropriate framework for the present project which follows the results obtained with the previous project ISOBIOTOX (PNRA 2013) and aims at (i) determine topological and functional metrics of sympagic and pelagic food webs at Terra Nova Bay under different conditions of sea-ice coverage along a distance gradient from the nearest open water polynya to areas were the seasonal sea-ice coverage persists longer; (ii) evaluate bioaccumulation and biomagnification of heavy metals in trophic sources at the base of the food web and in target species along food chains, including fishes of commercial interests and top predators, both in the presence and absence of sympagic and pelagic primary producers. High resolution food webs will be reconstructed by means of the simultaneous elemental and isotopic analysis of different elements (C and N) and the bioaccumulation of pollutants. The research program integrates complementary research approaches: (a) Elemental analysis coupled with mass spectrometry for stable isotope analysis (δ13C, δ15N) in animal and vegetal tissues and dead organic matter, (b)analyses of heavy metals accumulation (Chromatography) in the constituent species of the Antarctic food web.
-

The main goal of our proposal is to characterize the surface radiative budget as well as cloudiness which features at the Argentine Bases Marambio and Belgrano II during the YOPP-SH Special Observing Period (SOP) as well as the YOPP Consolidation Phase. Specific objectives to secure our main goal during the SOP will be: 1 - develop a compact Radiation Measurement UNIT (RMU) robust enough to allow continuous measurements in harsh environment through which to make shortwave, longwave observations as well as to record status of the sky. 2 - secure UV measurements at both stations. 3 - develop specific tools to analyse on a daily basis (weakly for clouds) collected data and extract parameters of interest. For radiation these will include QA/QC SW and LW downwelling and upwelling fluxes, diffuse and direct components of solar radiation, UV spectral flux and doses. For clouds these will include, on a continuous base, cloud fraction derived both from radiometric measurement and sky camera observations, cloud type and cloud effect on SW radiation. In addition cloud base (or cloud ceiling) will be obtained by routine observations performed at the two stations. From UV measurements columnar ozone content will be also derived. Moving forward to YOPP consolidation phase, we plan to: 1 - extend dataset and its analysis, start to collect information on seasonal and inter-annual variability, determine Cloud radiative Forcing (CRF) 2 - perform extensive comparison between automatic and visual cloudiness observation methods. They being very useful to better understand quality and value of historical datasets at the two stationsù 3 - make comparison with cloudiness regime of Ross Sea and Antarctic Plateau. Make similar comparison for UV fluxes in the Peninsula and at Concordia.
-
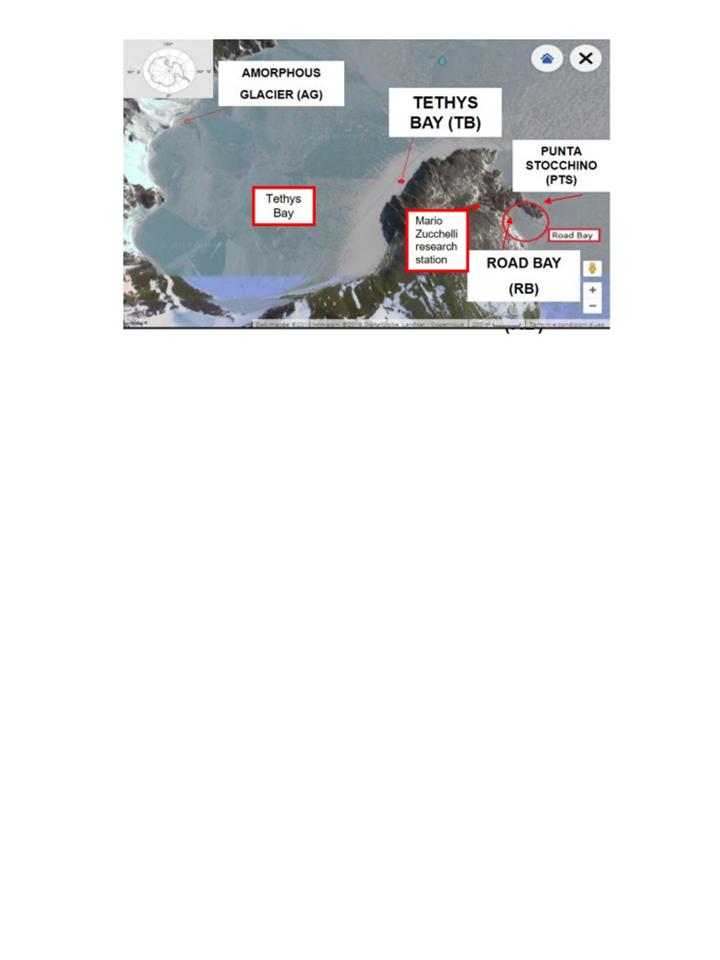
The ANT-Biofilm research project (PNRA16_00105) concerned the study of microbial colonization processes in coastal environments of Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea), through the analysis of the microbial biofilm (bacteria, microalgae) and macrobenthic settlement on plastic substrates, with the aim of determining their possible variations caused by natural or anthropogenic disturbances (variations in salinity or the presence of contaminants, respectively). Microbial biofilms, which play a key role as a substrate for larval settlement of many species of invertebrates, constitute hot-spots of microbial diversity; and it is also known that the communities a microbial are capable of responding rapidly to changing environmental conditions, acting as potential "sentinels" of natural or anthropic perturbations that recently are threatening the Antarctic biota. During the first year of activity (XXXIII Italian expedition, November 2017) stainless steel structures were fixed on the seabed of Road Bay and Tethys Bay mounting panels of artificial substrates (Polyvinyl Chloride, PVC and PolyEthylene, PE) for colonization, which during the XXXIV expedition (November 2018) were retrieved in order to study the fouling formation processes at different levels of biological complexity (from microbial community including bacteria and microalgae to benthic invertebrates) and to evaluate their evolution in two coastal sites differently exposed to natural or anthropogenic forcings.
-

The RESTORE project is dedicated to the development of portable robotic technologies with the capability to perform multi-disciplinary multi-parametric 3-D monitoring of marine environment. Its primary focus lies in examining critical areas such as the air-sea-ice and water-sediment interfaces in Antarctica. This endeavour aims to support various research aspects, including the study of microbial ecology and DNA tracing, as well as the investigation of Antarctic geology, particularly the dynamics surrounding glaciers and ice-covered coastal regions. Furthermore, RESTORE is committed to scrutinising the impacts of climate change on the Antarctic atmosphere and the exchanges that occur between the sea and air. The comprehensive dataset collected during RESTORE will provide researchers with a holistic perspective on an extreme and remote environment such as Antarctica, facilitating the interpretation of atmospheric and oceanic dynamics at the interface zones and, the 3D mapping of the underwater environment and the physical characterisation of the sampled region.