Dome C
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
Here we present the snow pits collected along the international EAIIST project traverse, which took place in 2019-2020 Antarctic Campaign. We report the number of snow pits collected, the depth of the samplings and their geographic information.
-
Here we present the surface snow samples collected along the international EAIIST project traverse, which took place in 2019-2020 Antarctic Campaign. We report the number of surface samples (upper 10 cm and integrated 1m samples) collected and their geographic information.
-
Here we present the firn cores collected along the international EAIIST project traverse, which took place in 2019-2020 Antarctic Campaign. We report the number of firn cores collected, the depth of the samplings and their geographic information.
-
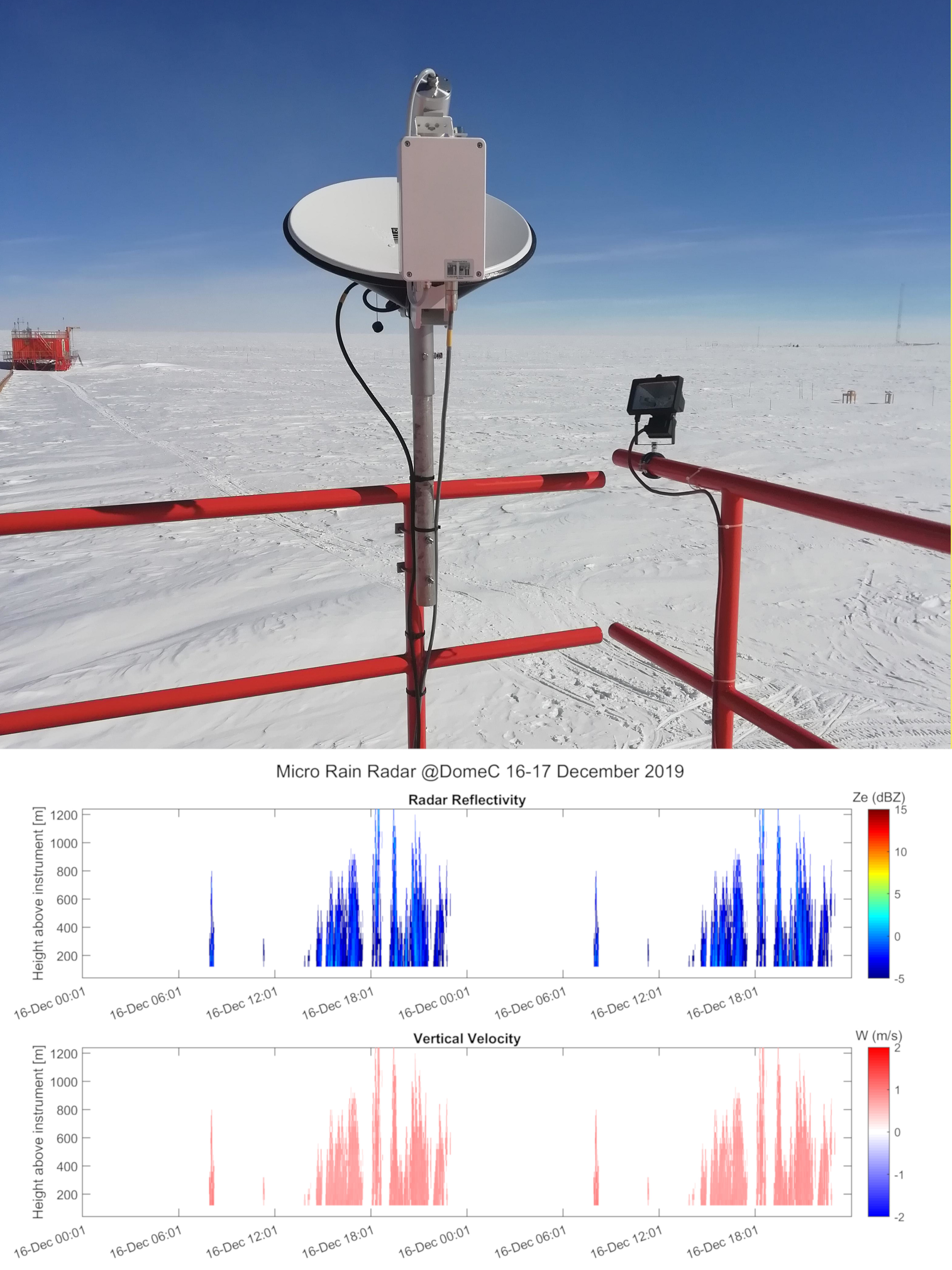
Vertical profiles along the first three kilometres of atmosphere above the ground (from 300 to 3000 m a.g.l.) of equivalent radar reflectivity factor (Ze), Doppler velocity (W) and Doppler spectral width (Sw) from a 24-GHz vertically pointing Micro Rain Radar MRR-2 by METEK GmbH positioned at Concordia Station (Dome C, Antarctica). The main objective of the FIRCLOUDS project is a complete spectral characterization of cirrus and mixed phase clouds in order to evaluate the radiative models in the FIR regime, where the clouds effect is very strong, and systematic spectral measurements are scarcely available. The micro rain radar (MRR) data allows the determination of the clouds reflectivity and the vertical velocity of ice crystals in the cases of precipitating clouds.
-

Pictures of the ice camera and the halo camera positioned at Concordia Station (Dome C, Antarctica). Data are available on the INO-CNR server on request to Dr. Massimo Del Guasta. The main objective of the FIRCLOUDS project is a complete spectral characterization of cirrus and mixed phase clouds in order to evaluate the radiative models in the FIR regime, where the clouds effect is very strong, and systematic spectral measurements are scarcely available. The ice and halo imager cameras enable an assessment of the cloud ice crystals micro-physics.
-
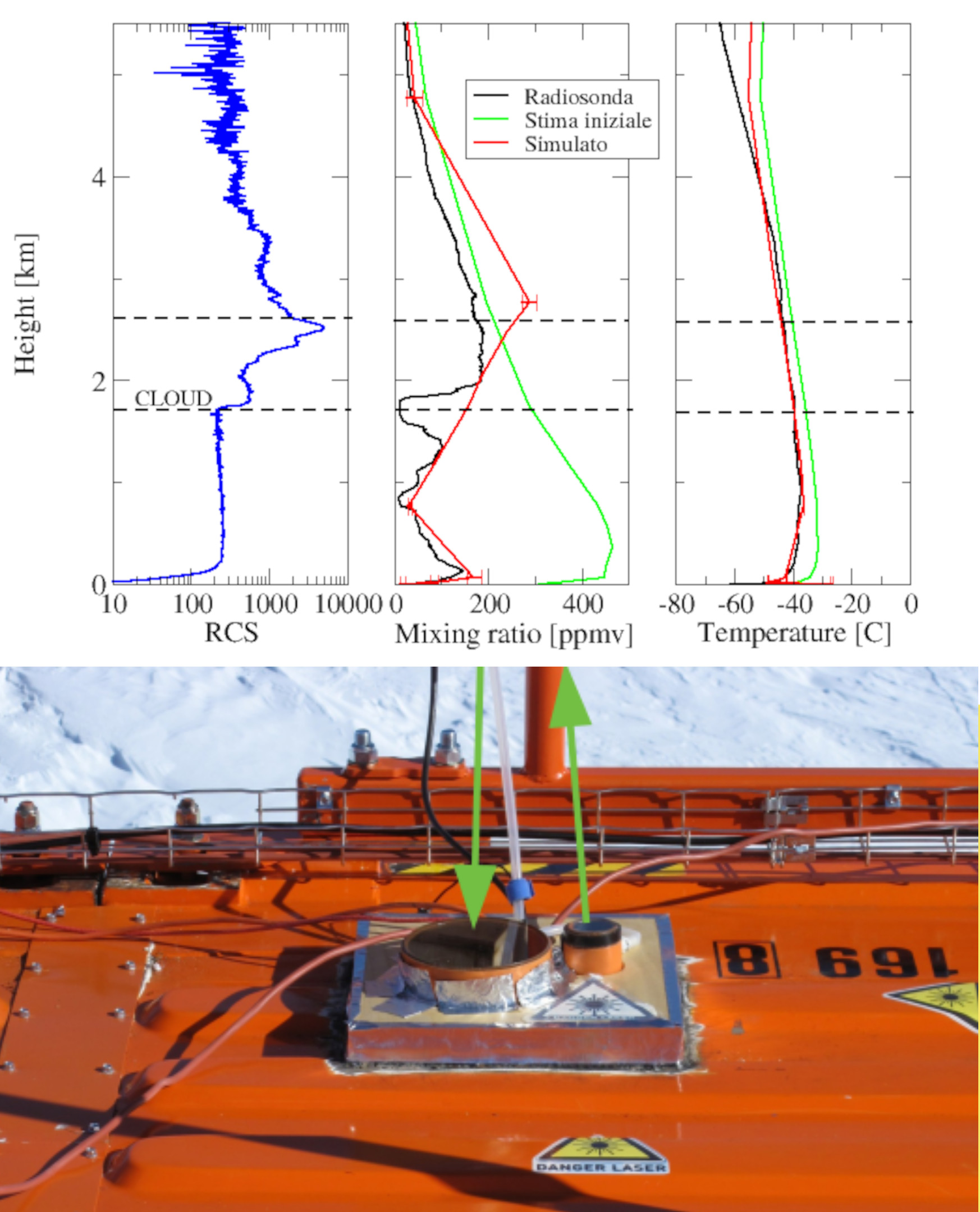
Backscattering and depolarization data from a LIDAR positioned at Concordia Station (Dome C, Antarctica). Data are available on the INO-CNR server on request to Dr. Massimo Del Guasta. The main objective of the FIRCLOUDS projectis a complete spectral characterization of cirrus and mixed phase clouds in order to evaluate the radiative models in the FIR regime, where the clouds effect is very strong, and systematic spectral measurements are scarcely available. A backscattering/depolarization lidar contributes to the estimation of the clouds position and phase, and of the optical extinction profile.