CNR - Consiglio nazionale delle ricerche
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
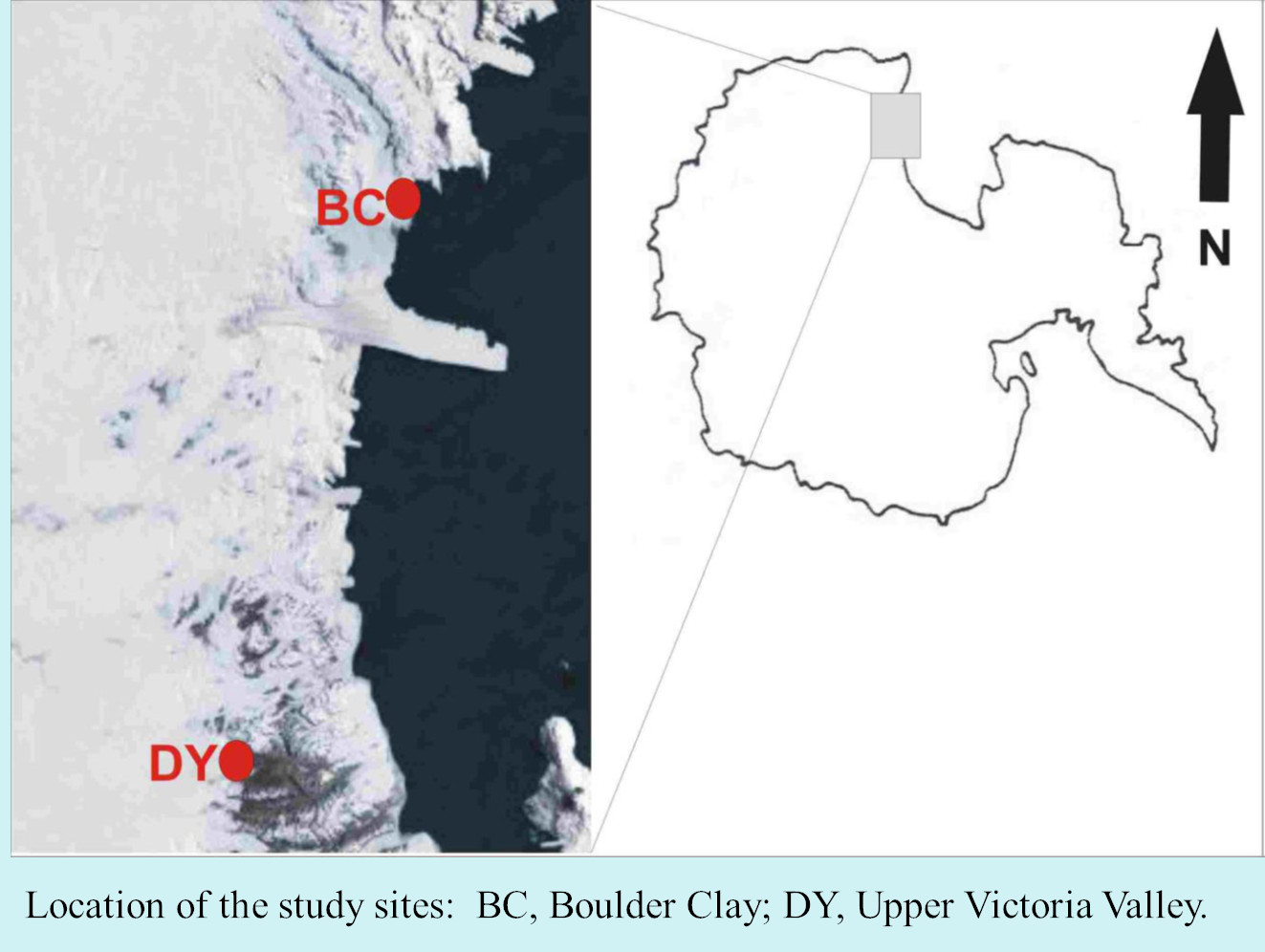
Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), characterized by a moltitude of ice tongues flowing from land to sea, represents an ideal study site for understanding the complex interaction between relative sea level variations and ice sheet dynamics during the Holocene. The DISGELI project, thanks to the combination of innovative technology and traditional methods for geomorphologic and stratigraphic analysis, aims to: i) reconstruct the local variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet after the Last Glacial Maximum; ii) provide a time constrain for the deglaciation processes along the coast; iii) reconstruct, with unprecedent detail, the relative sea level variations during Holocene in the Drygalski basin. The morpho-bathymetric and topographic data obtained through this study will be integrated using digital terrain models based on the analyses of key areas onland, where palaeo-coastlines and sea-level markers have been identified.
-
Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), characterized by a moltitude of ice tongues flowing from land to sea, represents an ideal study site for understanding the complex interaction between relative sea level variations and ice sheet dynamics during the Holocene. The DISGELI project, thanks to the combination of innovative technology and traditional methods for geomorphologic and stratigraphic analysis, aims to: i) reconstruct the local variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet after the Last Glacial Maximum; ii) provide a time constrain for the deglaciation processes along the coast; iii) reconstruct, with unprecedent detail, the relative sea level variations during Holocene in the Drygalski basin. The morpho-bathymetric and topographic data obtained through this study will be integrated using digital terrain models based on the analyses of key areas onland, where palaeo-coastlines and sea-level markers have been identified.
-
Permafrost hosts a potentially large pool of microorganisms, which is supposed to be the only life forms known to have retained viability over geological time. Thawing of the permafrost renews their physiological activity and exposes ancient life to modern ecosystems (Gilichinsky et al, 2008). The adaptation mechanisms of microorganisms, at species or population level, make them susceptible to extreme environmental conditions. The survival of microorganisms in permafrost raises the question of what constitutes the limit for microbial life (Steven et al., 2006; Wagner 2008).
-

The datataset includes sound pressure levels acquired in the Ross Sea during project AMORS
-
Surface ozone data, collected through a UV-absorption analyzer (49i or 49c)
-

The effects of sea ice melting, and the consequent changes in the trophic conditions in Antarctic ecosystems, have been focused on phytoplankton with cross-food web links from krill to penguins, while the consequences on the planktonic microbial food web (viruses, prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes), driving biogeochemical cycles, have been largely ignored. This research investigates how changes related to sea ice melting influence the diversity and functioning of planktonic microbes in the Ross Sea coastal ecosystem of Terranova Bay. The objectives are: i) to investigate the temporal changes of planktonic microbial biodiversity, ii) to investigate the biodiversity/ecosystem functioning relationships iii) to assess the role of viruses on biodiversity and biogeochemical cycles, iv) to identify the drivers that shape microbial biodiversity and functions, and v) to shed light on the interactions within the planktonic food web, and their response to the ice melting. META-ICE-ROSS integrates ad hoc sampling with sophisticated methodologies of high-throughput sequencing of microbial DNA (metagenomics), never documented in previous Italian expeditions at Terranova Bay. The sampling includes the collection of seawater beneath the pack ice at increasing distance from the MZ Station and characterised by different thermohaline conditions, on a weekly basis from early November to mid January. The groundbreaking nature of META-ICE-ROSS will allow to provide unprecedented evidences on the role of microbial interactions in the functioning of the Ross Sea coastal ecosystem, to improve knowledge on biological changes due to global climate changes and, nonetheless, to provide a baseline assessment of the functioning of the microbial food webs and carbon sequestration in the pelagic environment in the Ross Sea region, within the context of the Ross Sea Region Marine Protected Area (RSRMPA) and its monitoring and research plan.
-
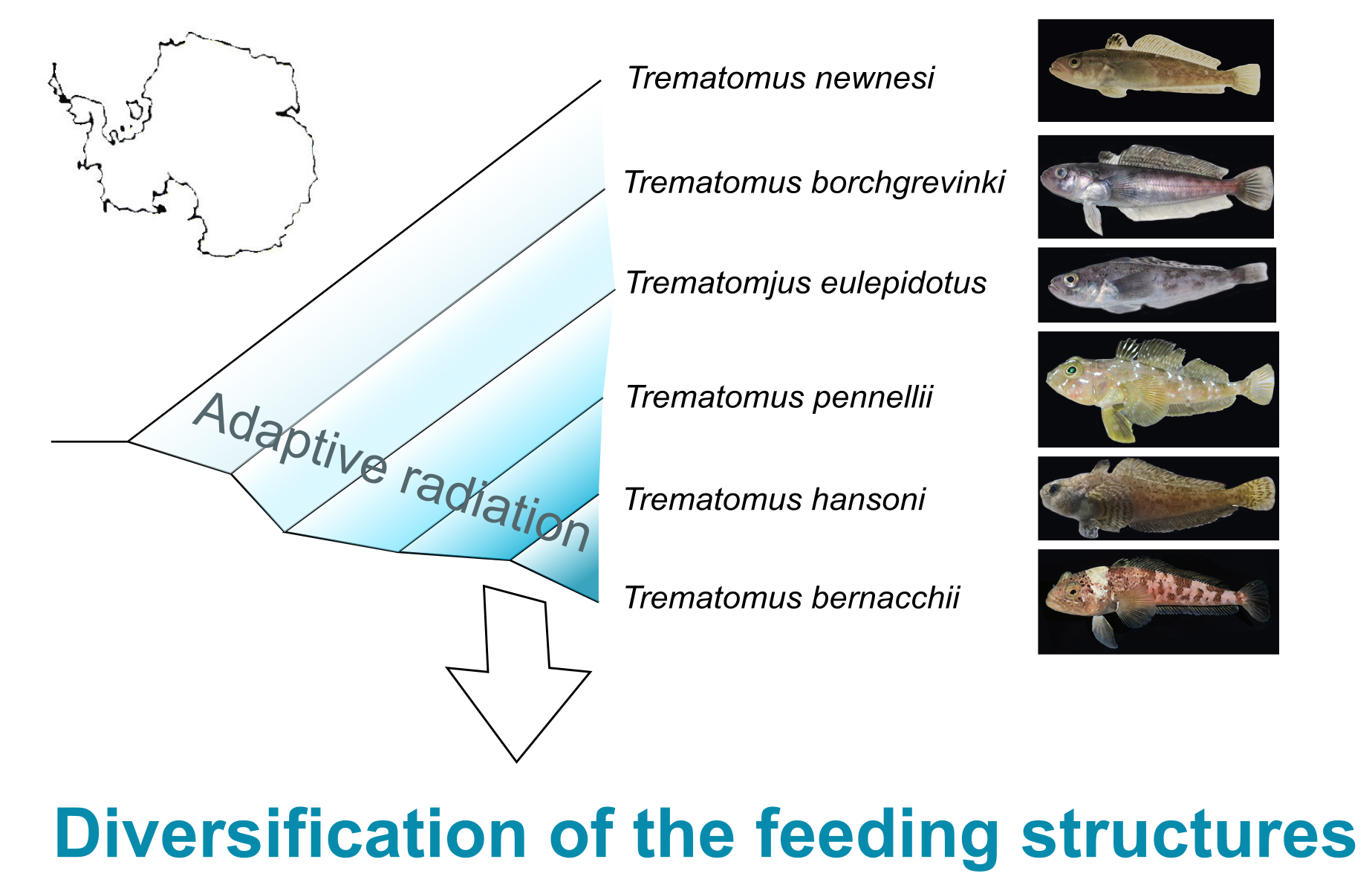
The EMPHASIS project focuses on the ecomorphology of the feeding apparatus of Notothenioidea, a suborder of teleost fishes endemic to the Southern Ocean that have colonized available ecological niches and habitats during their adaptive radiation. Ecomorphology is the science that investigates the reciprocal relationship between the environment and the forms of organisms, allowing insights into their evolutionary history, biodiversity, and relationships between form and function. The research activity involves a comparative analysis of the feeding apparatus in species representative of various phyletic lineages, and the study of the relationships between morphology, function and specific performance during feeding. Based on the results of the analysis, three-dimensional digitally supported models of the structures involved in feeding activity was developed.