Habitats and biotopes
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
The larval stages can be considered as the link from plankton to benthos. In order to study larval recruitment from zoobenthos, 40 tiles were placed at each of the four sites outlined in the project: Tethys Bay (control), Rod Bay (area subject to anthropogenic impact), Faraglione (control) and Adelie Cove (area subject to natural impact, linked to the presence of a penguin house). Due to adverse environmental factors all the tiles from Faraglione were lost and from Tethys Bay only half were found. The tiles were analysed with the help of a binocular, which enabled better visualisation of the organisms and, consequently, better identification.
-
Antarctic ecosystems have a high number of species, that are closely linked to the presence of sea ice and seasonal cycles. This biodiversity is subject to anthropogenic and natural influences. Macrozoobenthic communities are the 'biological memory' of the ecosystem, structuring themselves as a function of environmental changes over the years. Macrozoobenthos samples were collected using suction dredging and scraping techniques, in soft and hard bottoms. Sampling occurred in 5 different sites.
-
Antarctic ecosystems have a high number of species, that are closely linked to the presence of sea ice and seasonal cycles. This biodiversity is subject to anthropogenic and natural influences. Zooplankton communities can provide a static snapshot of the health of the ecosystem. Zooplankton samples were collected with a 200 μm mesh net at 3 different sampling points at 80 m depth.
-
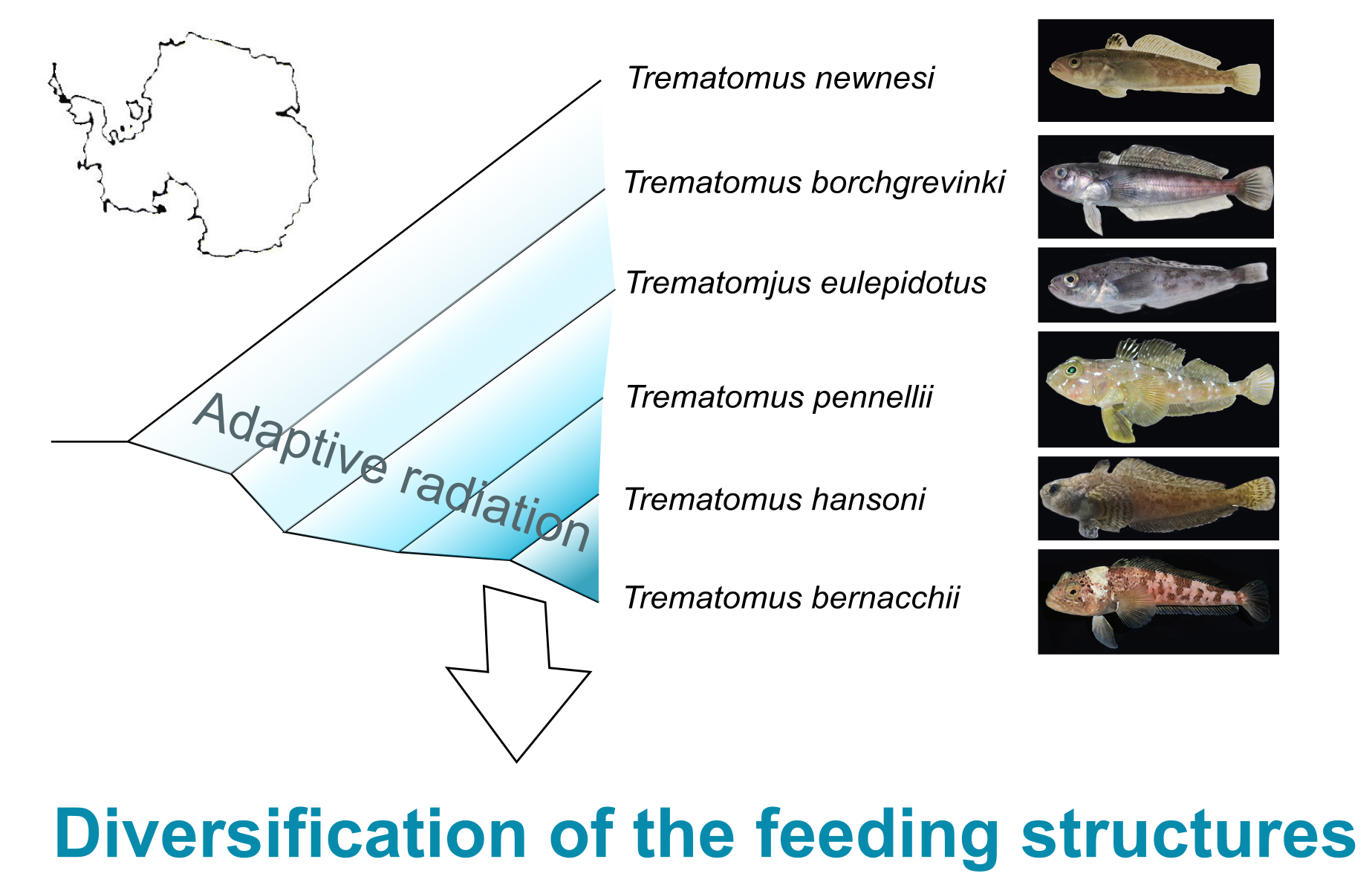
The EMPHASIS project focuses on the ecomorphology of the feeding apparatus of Notothenioidea, a suborder of teleost fishes endemic to the Southern Ocean that have colonized available ecological niches and habitats during their adaptive radiation. Ecomorphology is the science that investigates the reciprocal relationship between the environment and the forms of organisms, allowing insights into their evolutionary history, biodiversity, and relationships between form and function. The research activity involves a comparative analysis of the feeding apparatus in species representative of various phyletic lineages, and the study of the relationships between morphology, function and specific performance during feeding. Based on the results of the analysis, three-dimensional digitally supported models of the structures involved in feeding activity was developed.
-

Trophic interactions underlie coexistence mechanisms between species, define the functional role of specie within communities, affect biodiversity and bioaccumulation processes of heavy metal. Sea-ice dynamics, which at Terra Nova Bay is characterized by an extraordinary seasonality, drives interspecific interactions and the exchange of materials between ecosystem compartments. Indeed, the activation of the primary production after sea-ice break up opens alternative trophic pathways for consumers. The “next generation SRPs” represent a highly appropriate framework for the present project which follows the results obtained with the previous project ISOBIOTOX (PNRA 2013) and aims at (i) determine topological and functional metrics of sympagic and pelagic food webs at Terra Nova Bay under different conditions of sea-ice coverage along a distance gradient from the nearest open water polynya to areas were the seasonal sea-ice coverage persists longer; (ii) evaluate bioaccumulation and biomagnification of heavy metals in trophic sources at the base of the food web and in target species along food chains, including fishes of commercial interests and top predators, both in the presence and absence of sympagic and pelagic primary producers. High resolution food webs will be reconstructed by means of the simultaneous elemental and isotopic analysis of different elements (C and N) and the bioaccumulation of pollutants. The research program integrates complementary research approaches: (a) Elemental analysis coupled with mass spectrometry for stable isotope analysis (δ13C, δ15N) in animal and vegetal tissues and dead organic matter, (b)analyses of heavy metals accumulation (Chromatography) in the constituent species of the Antarctic food web.
-

Trophic interactions underlie coexistence mechanisms between species and affect biodiversity and heavy metal bioaccumulation processes. Sea ice dynamics, which at Terra Nova Bay is characterized by an extraordinary seasonality, drives interspecific interactions. Indeed, the activation of the primary production after sea-ice break up opens alternative trophic pathways for consumers. By means of C and N stable isotope analyses, the present project aims at (i) determining food web structure at Terra Nova Bay at different bathymetries and in opposite sea-ice cover conditions; (ii) evaluating heavy metal bioaccumulation in species along food chains, including fish of commercial interests, both in the presence and absence of photosynthetic primary producers. The hypothesis to be tested is if the activation of primary producers following sea-ice break up significantly modifies the food web structure and stability against species loss, as well as heavy metals concentration along food chains. Data on Antarctic food webs are scarce, and even scarcer is our knowledge on mechanisms of primary and secondary biodiversity loss and biomagnification processes in invertebrates and fish. The present research project will shed light on mechanisms underlying biodiversity maintenance in the Antarctic ecosystem and on risks for human health related to heavy metals accumulation in fish species currently or potentially exploited commercially, also in light of expected changes in the extension of sea ice cover. A valuable reference baseline will be established for future studies at the Italian Antarctic Station and for the Marine Protected Area in the Ross Sea.
-

The RESTORE project is dedicated to the development of portable robotic technologies with the capability to perform multi-disciplinary multi-parametric 3-D monitoring of marine environment. Its primary focus lies in examining critical areas such as the air-sea-ice and water-sediment interfaces in Antarctica. This endeavour aims to support various research aspects, including the study of microbial ecology and DNA tracing, as well as the investigation of Antarctic geology, particularly the dynamics surrounding glaciers and ice-covered coastal regions. Furthermore, RESTORE is committed to scrutinising the impacts of climate change on the Antarctic atmosphere and the exchanges that occur between the sea and air. The comprehensive dataset collected during RESTORE will provide researchers with a holistic perspective on an extreme and remote environment such as Antarctica, facilitating the interpretation of atmospheric and oceanic dynamics at the interface zones and, the 3D mapping of the underwater environment and the physical characterisation of the sampled region.