IT/PNRA
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Scale
-
BRIEF NARRATIVE SUMMARY OF THE CONTENT OF THE RESOURCES(S)
-
The data are related to the ionic composition of atmospheric aerosol continuously collected at Dome C. They refer to PM10 and size-segregated aerosol collected at 2-day and 4-day resolution, respectively. The measured chemical parameters include main and trace inorganic anions and cations and selected organic anions (methanesulphonic acid - MSA).
-

The knowledge of properties and quantitative measurement of solid precipitation in Antarctica is of fundamental importance as precipitation represents the main input of Antarctic ice sheet mass, the variations of which have a direct and non-negligible effect on the average level of the oceans at global scale. Characterization and quantification of the precipitation is crucial in defining and validating global climate models and numerical weather prediction models, as well as anchoring and validating space-borne remote sensing estimates from missions like CloudSAT and EarthCARE. A snow and cloud microphysics observatory has been set up at the Italian Antarctic station Mario Zucchelli (MZS), integrating the pre-existing instrumentation for weather measurements. In particular, a 24-GHz vertical pointing Doppler radar, the METEK's Micro Rain Radar 2 (MRR-2), and a laser disdrometer, the OTT Parsivel, have been integrated with the advanced weather stations, radiosoundings and the ceilometer already present at MZS. The synergy between the set of instruments allows for characterizing precipitation and studying properties of Antarctic precipitation such as dimension, shape, fall behavior, particle number density, particles size distribution, particles terminal velocity, reflectivity factor and information on their vertical extent. APP started as a four-year project in July 2017, covering the Special Observation Period (SOP) in the Southern Hemisphere of Year of Polar Predicition (YOPP) period. APP can provide specific measurements for precipitation occurring over the Antarctic coast at high temporal resolution, in particular specific snow products such as snow rate, snow depth and their water equivalent. In November 2023 the observatory received an additional instrument, the Thies Clima 3D Stereo imaging disdrometer, which was previously installed for one year in Italy for testing, at the Casale Calore (AQ) meteorological observation site from the University of L'Aquila. The research team of the first two years was coordinated by Nicoletta Roberto, with operational units at the Rome unit of the CNR-ISAC (Luca Baldini, Elisa Adirosi, Stefano Dietrich) and at the Department of Physics and Astronomy of the University of Bologna (Rolando Rizzi, Federico Porcù, Tiziano Maestri, Alessandro Bracci). From 2020 the coordination of the project passed to Luca Baldini (CNR-ISAC) and the work team was extended with the research fellows Giacomo Roversi and Sabina Angeloni.
-
Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), characterized by a moltitude of ice tongues flowing from land to sea, represents an ideal study site for understanding the complex interaction between relative sea level variations and ice sheet dynamics during the Holocene. The DISGELI project, thanks to the combination of innovative technology and traditional methods for geomorphologic and stratigraphic analysis, aims to: i) reconstruct the local variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet after the Last Glacial Maximum; ii) provide a time constrain for the deglaciation processes along the coast; iii) reconstruct, with unprecedent detail, the relative sea level variations during Holocene in the Drygalski basin. The morpho-bathymetric and topographic data obtained through this study will be integrated using digital terrain models based on the analyses of key areas onland, where palaeo-coastlines and sea-level markers have been identified.
-
Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), characterized by a moltitude of ice tongues flowing from land to sea, represents an ideal study site for understanding the complex interaction between relative sea level variations and ice sheet dynamics during the Holocene. The DISGELI project, thanks to the combination of innovative technology and traditional methods for geomorphologic and stratigraphic analysis, aims to: i) reconstruct the local variations of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet after the Last Glacial Maximum; ii) provide a time constrain for the deglaciation processes along the coast; iii) reconstruct, with unprecedent detail, the relative sea level variations during Holocene in the Drygalski basin. The morpho-bathymetric and topographic data obtained through this study will be integrated using digital terrain models based on the analyses of key areas onland, where palaeo-coastlines and sea-level markers have been identified.
-

Emerging COntaminants in Antarctic Snow: sources and TRAnsport (ECO AS:TRA) Prog. PNRA18_00229 Snow samples
-
De novo transcriptome analysis of Colobanthus quitensis Antarctic vascular plant grown under condition miming the global warm-up.
-
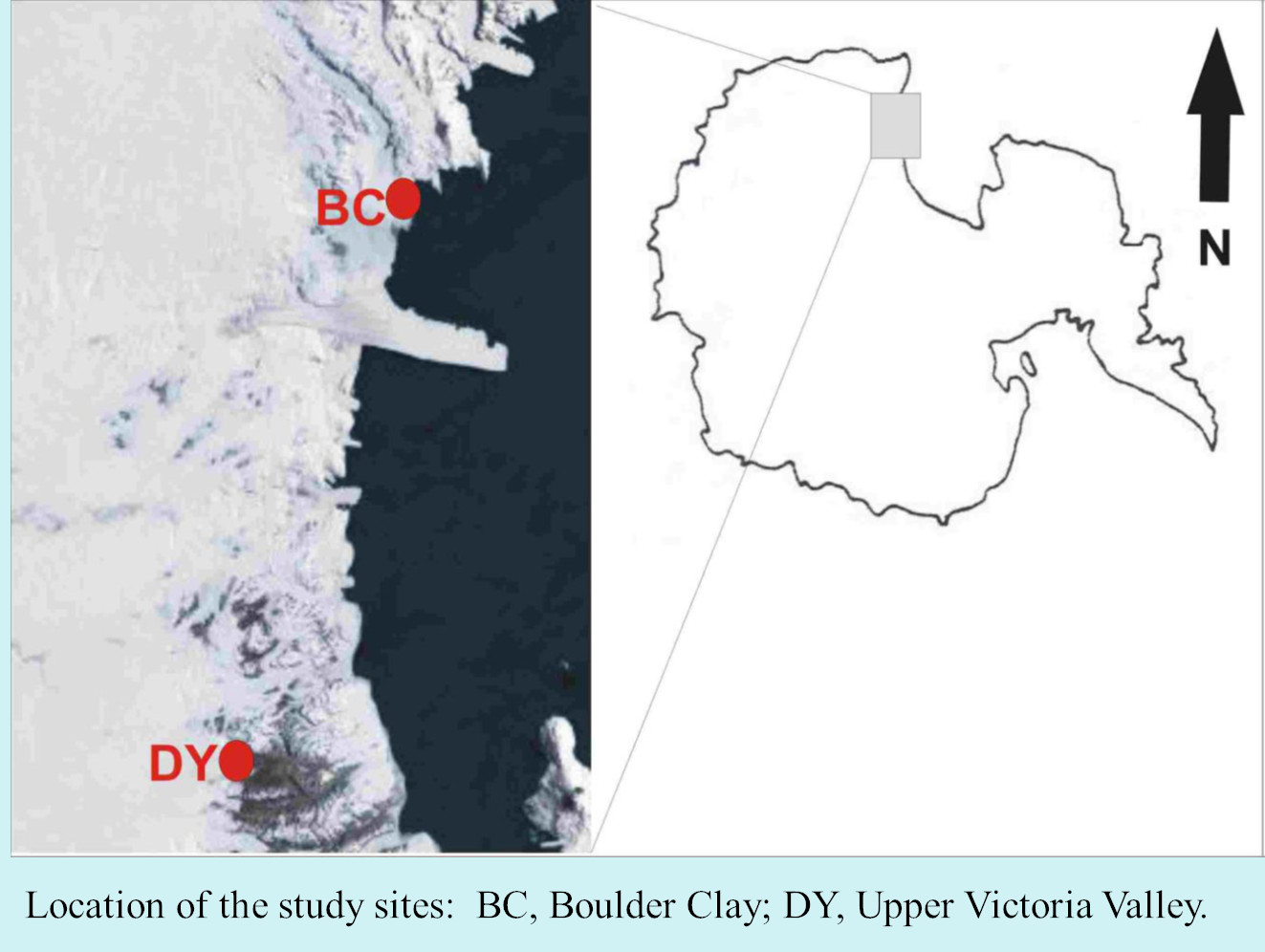
Permafrost hosts a potentially large pool of microorganisms, which is supposed to be the only life forms known to have retained viability over geological time. Thawing of the permafrost renews their physiological activity and exposes ancient life to modern ecosystems (Gilichinsky et al, 2008). The adaptation mechanisms of microorganisms, at species or population level, make them susceptible to extreme environmental conditions. The survival of microorganisms in permafrost raises the question of what constitutes the limit for microbial life (Steven et al., 2006; Wagner 2008).
-
Calibrated (in unit of solar disk brightness) measurements of the sky brightness at DOME C as obtained by the ESCAPE experiment during the campaign 2018-2019
-
Calibrated (in unit of solar disk brightness) measurements of the sky brightness at DOME C as obtained by the ESCAPE experiment during the campaign 2022-2023